一些小提示和小技巧可能是非常有用的,特别是在编程领域。有时候使用一点点黑客技术,既可以节省时间,还可能挽救“生命”。
一个小小的快捷方式或附加组件有时真是天赐之物,并且可以成为真正的生产力助推器。所以,这里有一些小提示和小技巧,有些可能是新的,但我相信在下一个数据分析项目中会让你非常方便。
Pandas中数据框数据的Profiling过程
Profiling(分析器)是一个帮助我们理解数据的过程,而Pandas Profiling是一个Python包,它可以简单快速地对Pandas 的数据框数据进行探索性数据分析。
Pandas中df.describe()和df.info()函数可以实现EDA过程第一步。但是,它们只提供了对数据非常基本的概述,对于大型数据集没有太大帮助。而Pandas中的Profiling功能简单通过一行代码就能显示大量信息,且在交互式HTML报告中也是如此。
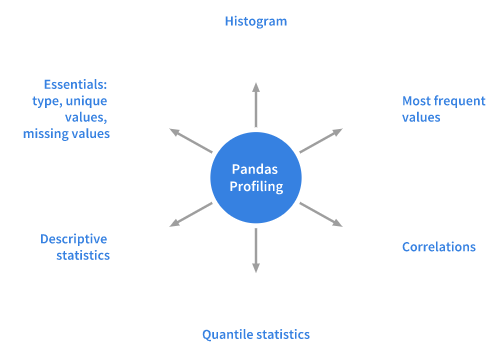
对于给定的数据集,Pandas中的profiling包计算了以下统计信息:
由Pandas Profiling包计算出的统计信息包括直方图、众数、相关系数、分位数、描述统计量、其他信息——类型、单一变量值、缺失值等。
安装
用pip安装或者用conda安装
<span class="code-snippet_outer">pip install pandas-profiling</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> conda install -c anaconda pandas-profiling</span>
用法
下面代码是用很久以前的泰坦尼克数据集来演示多功能Python分析器的结果。
<span class="code-snippet_outer">#importing the necessary packages</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> import pandas as pd</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> import pandas_profiling</span><span class="code-snippet_outer">df = pd.read_csv('titanic/train.csv')</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> pandas_profiling.ProfileReport(df)</span>
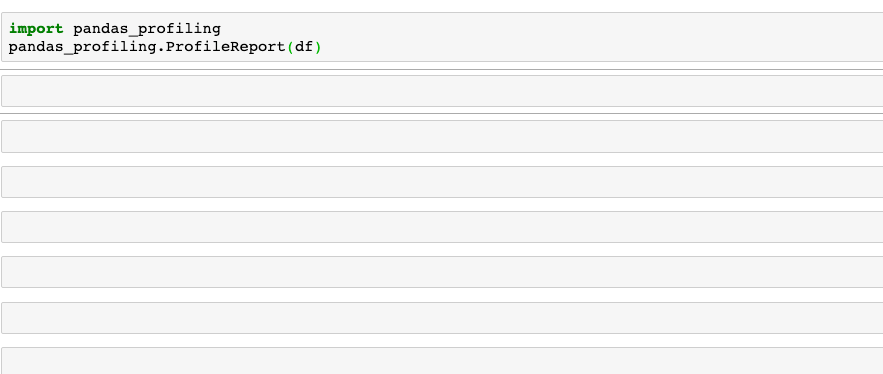
一行代码就能实现在Jupyter Notebook中显示完整的数据分析报告,该报告非常详细,且包含了必要的图表信息。
还可以使用以下代码将报告导出到交互式HTML文件中。
<span class="code-snippet_outer">profile = pandas_profiling.ProfileReport(df)</span><span class="code-snippet_outer">profile.to_file(outputfile="Titanic data profiling.html")</span>
Pandas实现交互式作图
Pandas有一个内置的.plot()函数作为DataFrame类的一部分。但是,使用此功能呈现的可视化不是交互式的,这使得它没那么吸引人。同样,使用pandas.DataFrame.plot()函数绘制图表也不能实现交互。如果我们需要在不对代码进行重大修改的情况下用Pandas绘制交互式图表怎么办呢?这个时候就可以用Cufflinks库来实现。
Cufflinks库可以将有强大功能的plotly和拥有灵活性的pandas结合在一起,非常便于绘图。下面就来看在pandas中如何安装和使用Cufflinks库。
安装
<span class="code-snippet_outer">pip install plotly</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"># Plotly is a pre-requisite before installing cufflinks</span><span class="code-snippet_outer">pip install cufflinks</span>
用法
<span class="code-snippet_outer">#importing Pandas </span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> import pandas as pd</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> #importing plotly and cufflinks in offline mode</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> import cufflinks as cf</span><span class="code-snippet_outer">import plotly.offline</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> cf.go_offline()</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> cf.set_config_file(offline=False, world_readable=True)</span>
是时候展示泰坦尼克号数据集的魔力了。
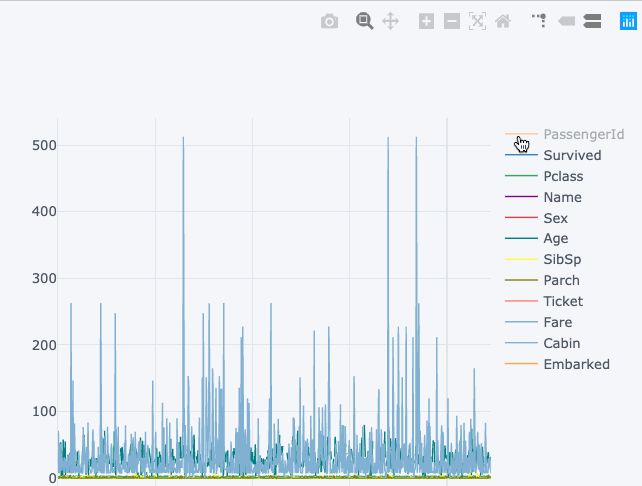
<span class="code-snippet_outer">df.iplot()</span>
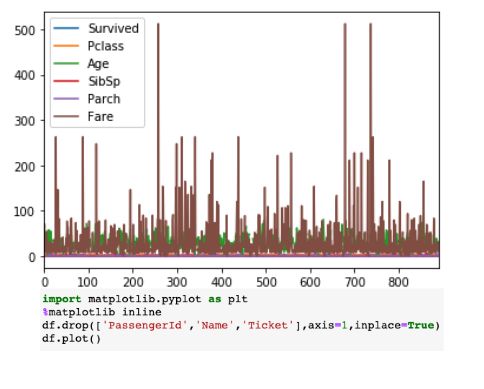
<span class="code-snippet_outer">df.iplot() vs df.plot()</span>
右侧的可视化显示了静态图表,而左侧图表是交互式的,更详细,并且所有这些在语法上都没有任何重大更改。
Magic命令
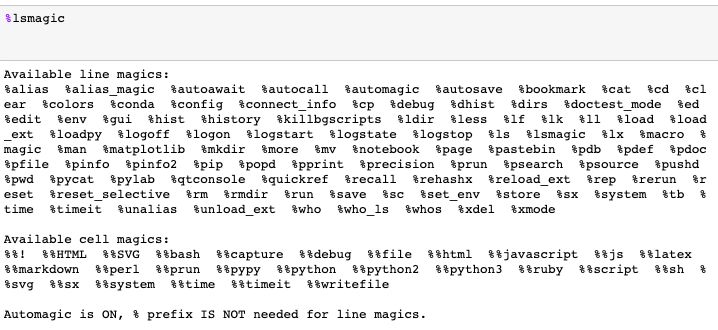
Magic命令是Jupyter notebook中的一组便捷功能,旨在解决标准数据分析中的一些常见问题。使用命令%lsmagic可以看到所有的可用命令。
所有可用的Magic命令列表
Magic命令有两种:行magic命令(line magics),以单个%字符为前缀,在单行输入操作;单元magic命令(cell magics),以双%%字符为前缀,可以在多行输入操作。如果设置为1,则不用键入%即可调用Magic函数。
接下来看一些在常见数据分析任务中可能用到的命令:
% pastebin
%pastebin将代码上传到Pastebin并返回url。Pastebin是一个在线内容托管服务,可以存储纯文本,如源代码片段,然后通过url可以与其他人共享。事实上,Github gist也类似于pastebin,只是有版本控制。
在file.py文件中写一个包含以下内容的python脚本,并试着运行看看结果。
<span class="code-snippet_outer">#file.py</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> def foo(x):</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> return x</span>
在Jupyter Notebook中使用%pastebin生成一个pastebin url。
%matplotlib notebook
函数用于在Jupyter notebook中呈现静态matplotlib图。用notebook替换inline,可以轻松获得可缩放和可调整大小的绘图。但记得这个函数要在导入matplotlib库之前调用。
%run
用%run函数在notebook中运行一个python脚本试试。
<span class="code-snippet_outer">%run file.py</span><span class="code-snippet_outer">%%writefile</span>
%% writefile是将单元格内容写入文件中。以下代码将脚本写入名为foo.py的文件并保存在当前目录中。
%%latex
%%latex函数将单元格内容以LaTeX形式呈现。此函数对于在单元格中编写数学公式和方程很有用。
查找并解决错误
交互式调试器也是一个神奇的功能,我把它单独定义了一类。如果在运行代码单元时出现异常,请在新行中键入%debug并运行它。这将打开一个交互式调试环境,它能直接定位到发生异常的位置。还可以检查程序中分配的变量值,并在此处执行操作。退出调试器单击q即可。
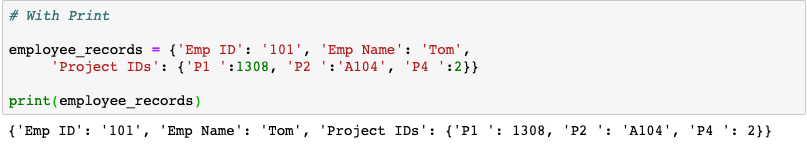
Printing也有小技巧
如果您想生成美观的数据结构,pprint是首选。它在打印字典数据或JSON数据时特别有用。接下来看一个使用print和pprint来显示输出的示例。
让你的笔记脱颖而出
我们可以在您的Jupyter notebook中使用警示框/注释框来突出显示重要内容或其他需要突出的内容。注释的颜色取决于指定的警报类型。只需在需要突出显示的单元格中添加以下任一代码或所有代码即可。
蓝色警示框:信息提示
<span class="code-snippet_outer"><div class="alert alert-block alert-info"></span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> <b>Tip:</b> Use blue boxes (alert-info) for tips and notes. </span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> If it’s a note, you don’t have to include the word “Note”.</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> </div></span>
黄色警示框:警告
<span class="code-snippet_outer"><div class="alert alert-block alert-warning"></span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> <b>Example:</b> Yellow Boxes are generally used to include additional examples or mathematical formulas.</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> </div></span>
绿色警示框:成功
<span class="code-snippet_outer"><div class="alert alert-block alert-success"></span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> Use green box only when necessary like to display links to related content.</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> </div></span>
红色警示框:高危
<span class="code-snippet_outer"><div class="alert alert-block alert-danger"></span><span class="code-snippet_outer">It is good to avoid red boxes but can be used to alert users to not delete some important part of code etc. </span><span class="code-snippet_outer"></div></span>
打印单元格所有代码的输出结果
假如有一个Jupyter Notebook的单元格,其中包含以下代码行:
<span class="code-snippet_outer">In [1]: 10+5 </span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> 11+6</span><span class="code-snippet_outer">Out [1]: 17</span>
单元格的正常属性是只打印最后一个输出,而对于其他输出,我们需要添加print()函数。然而通过在notebook顶部添加以下代码段可以一次打印所有输出。
添加代码后所有的输出结果就会一个接一个地打印出来。
<span class="code-snippet_outer">In [1]: 10+5 </span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> 11+6</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> 12+7</span><span class="code-snippet_outer">Out [1]: 15</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> Out [1]: 17</span><span class="code-snippet_outer"> Out [1]: 19</span>
恢复原始设置:
<span class="code-snippet_outer">InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "last_expr"</span>
使用'i'选项运行python脚本
从命令行运行python脚本的典型方法是:python hello.py。但是,如果在运行相同的脚本时添加-i,例如python -i hello.py,就能提供更多优势。接下来看看结果如何。
首先,即使程序结束,python也不会退出解释器。因此,我们可以检查变量的值和程序中定义的函数的正确性。
其次,我们可以轻松地调用python调试器,因为我们仍然在解释器中:
<span class="code-snippet_outer">import pdb</span><span class="code-snippet_outer">pdb.pm()</span>
这能定位异常发生的位置,然后我们可以处理异常代码。
自动评论代码
Ctrl / Cmd + /自动注释单元格中的选定行,再次命中组合将取消注释相同的代码行。
删除容易恢复难
你有没有意外删除过Jupyter notebook中的单元格?如果答案是肯定的,那么可以掌握这个撤消删除操作的快捷方式。
如果您删除了单元格的内容,可以通过按CTRL / CMD + Z轻松恢复它。
如果需要恢复整个已删除的单元格,请按ESC + Z或EDIT>撤消删除单元格。
结论
在本文中,我列出了使用Python和Jupyter notebook时收集的一些小提示。我相信它们会对你有用,能让你有所收获,从而实现轻松编码!
本文为原创文章,版权归知行编程网所有,欢迎分享本文,转载请保留出处!
















内容反馈